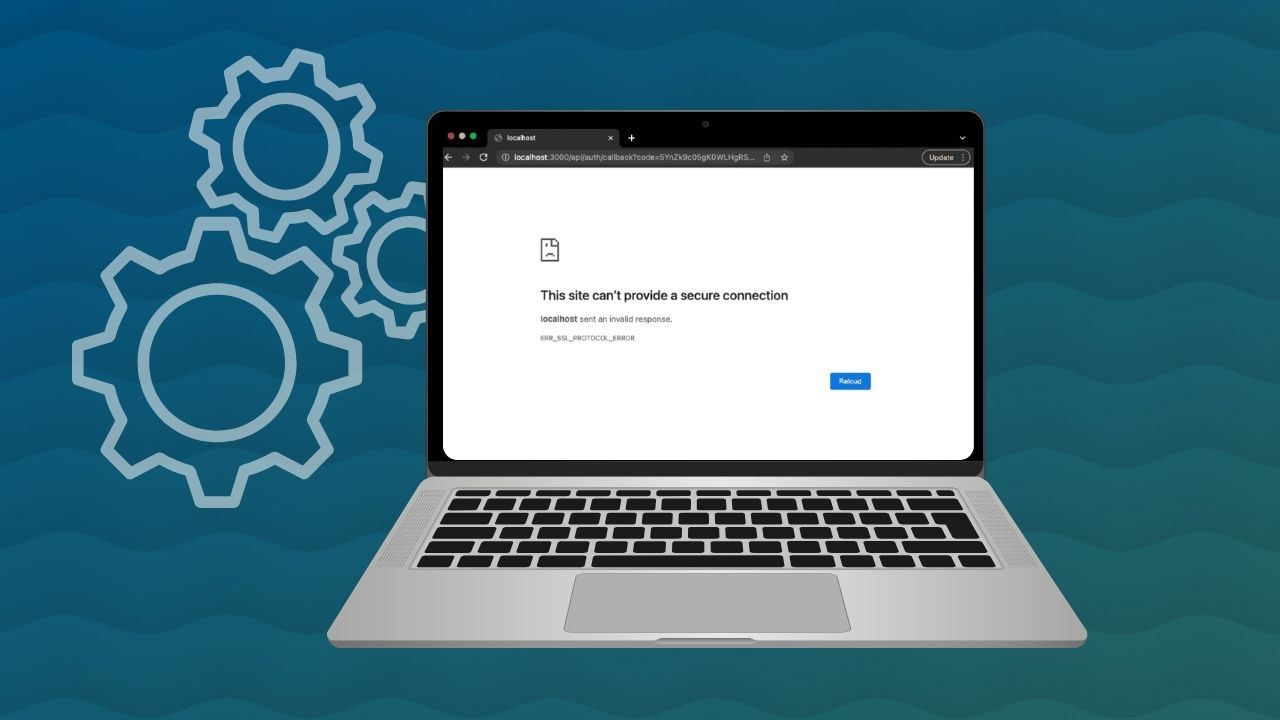
Seeing the “This site can’t provide a secure connection” error message can be frustrating, especially when you’re trying to access an important website. Modern browsers are designed to protect users from unsafe connections, and tools like Wave Browser include secure features that help flag potential risks before sensitive information is exposed.
This article explains what this secure connection error means, the most common reasons it appears, and what steps you can take to identify the culprit, whether it’s your browser, device settings, or the website itself.
How Do Secure Internet Connections Work?

When you visit a website that starts with https://, your browser tries to create a secure connection using security protocols called SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or, more commonly today, TLS (Transport Layer Security).
These protocols are designed to protect your data by encrypting information before it travels between your browser and the website.
To successfully establish a secure connection, a few things must work together.
A valid SSL/TLS certificate
The website must have a trusted certificate installed on its server to prove its identity. Your browser checks this certificate to make sure the site is legitimate and hasn’t been tampered with.
Compatible encryption methods
The browser and server must agree on how data will be encrypted. If the server uses outdated or unsupported security standards, the connection can fail.
Proper server configuration
The server must be set up correctly to handle secure connections, including certificate chains, encryption settings, and protocol support.
During this process, your browser and the server perform what’s called an SSL/TLS handshake—a quick exchange of information that verifies identity and sets up encryption.
If the browser can’t verify the certificate, agree on encryption, or complete this handshake safely, it will block the connection and display a secure connection error to protect your data.
What Does “This Site Can’t Provide a Secure Connection” Mean?

The error message “this site can’t provide a secure connection” usually appears when your web browser cannot establish a trusted, encrypted connection with a website.
Secure websites rely on HTTPS and SSL/TLS certificates to protect data sent between your device and the web server. When something goes wrong during that process, the browser blocks access to protect your personal data and online privacy.
Common Causes of Invalid and Secure Connection Errors
There are several common reasons why the "This site can’t provide a secure connection" error occurs. Some issues are on your device, while others are on the server side.
1. SSL Certificate Issues
The most frequent cause of "This site can’t provide a secure connection" is a problem with the website’s SSL certificate:
- Expired SSL certificate
- Invalid or misconfigured certificate
- Missing intermediate certificates
- Certificate issued for a different domain
Using an SSL checker tool can help website owners identify certificate problems.
2. Incorrect Date and Time Settings
Your device’s date settings, time settings, or time zone must be correct. An incorrect date can cause the browser to treat a valid certificate as expired or invalid.
This is a common culprit on:
- macOS systems
- Windows PCs
- Mobile devices after travel or manual changes
3. Browser Cache or SSL Cache Problems
A corrupted browser cache or SSL cache can interfere with SSL connections. Browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and others store SSL data to speed up future connections.
Clearing the cache often resolves temporary SSL errors.
4. Antivirus Software or Firewall Interference
Some antivirus programs, firewalls, or VPN tools inspect encrypted web traffic to detect threats. When these tools are misconfigured or overly restrictive, they can interfere with SSL/TLS encryption and prevent secure connections from completing properly—resulting in secure connection errors.
This type of interference may come from:
- Antivirus or internet security software
- VPN services
- Network-level firewalls (such as those used on work or public networks)
5. Browser Extensions Impacting HTTPS Connections
Browser extensions can be incredibly useful, but not all of them are built with security in mind.
Some extensions—especially outdated, poorly reviewed, or unofficial ones—can interfere with how your browser establishes secure HTTPS connections. This may happen if an extension modifies network traffic, injects scripts into web pages, or attempts to scan encrypted content.
6. Malware
Malware or malicious plugins pose a bigger risk. These can hijack connections, redirect traffic, or attempt to intercept secure data, triggering “Secure Connection Failed” or similar errors as your browser blocks unsafe activity.
To troubleshoot this issue:
- Try opening the site in incognito or private mode, where most extensions are disabled by default.
- If the site loads correctly, re-enable extensions one at a time to identify the culprit.
- Remove any extensions you don’t recognize, no longer use, or didn’t install intentionally.
- Run a trusted malware or security scan to rule out harmful software on your device.
Keeping your browser clean—by limiting extensions, reviewing permissions, and removing anything suspicious—helps ensure secure connections work as intended and reduces your overall risk online.
7. QUIC Protocol and UDP Issues
QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is a modern network protocol developed to make web connections faster and more reliable.
Instead of using the traditional TCP protocol, QUIC runs over UDP, allowing browsers to establish secure connections more quickly and reduce delays when loading websites. It also integrates encryption by default, which helps improve both speed and security.
To troubleshoot:
- Temporarily disable QUIC in your browser settings.
- Reload the website to see if the error disappears.
- If the site loads normally afterward, QUIC-related UDP restrictions are likely the cause.
In such cases, keeping QUIC disabled or switching to a different network can help restore a stable and secure browsing experience.
8. Server, Hosting, or DNS Problems
In some cases, a secure connection error isn’t caused by your browser or device at all—it originates on the website’s side. If the server can’t properly support secure HTTPS connections, your browser will block access to protect your data.
Common website-side causes include:
- Web server misconfiguration, such as incorrect SSL/TLS settings
- Hosting provider issues, including outages or mismanaged security updates
- DNS problems, where the domain name doesn’t correctly point to the server
- Outdated TLS certificates or missing SSL updates, which prevent proper encryption
When these issues occur, there’s little a visitor can do. The problem must be resolved by the website owner or their hosting provider, who can update certificates, fix server settings, or correct DNS records.
What Google Chrome, Wave, and Firefox Users Can Do

If you encounter the "this site can’t provide a secure connection" error, try the following:
- Check your internet connection
- Verify system date, time, and time zone
- Clear browser cache and SSL cache
- Disable browser extensions
- Test incognito mode
- Temporarily disable antivirus or VPN software
- Try another browser or device
If the issue persists across devices, it’s likely a server-side problem.
Tips for Website Owners
If you manage a site (for example, a WordPress site using a plugin), ensure:
- Your SSL certificate is valid and up to date
- A new SSL certificate is installed before expiration
- TLS configuration supports modern cipher suites
- Hosting and DNS settings are correct
Regular checks prevent users from encountering the error "this site can’t provide a secure connection" and other secure connection errors.
Why Secure Browsing Matters

Secure connections protect sensitive data, login credentials, and personal information.
Browsers with built-in security features help users navigate the internet with more confidence by identifying unsafe or misconfigured sites early. Tools like Wave Browser focus on secure, user-friendly browsing to help users avoid risky connections without disrupting everyday browsing.
The “This site can’t provide a secure connection” error is a protective measure, not just an inconvenience. Understanding the common reasons behind it helps you quickly determine whether the issue lies with your browser, device settings, or the website itself.
By staying aware of SSL certificate issues, browser configuration, and basic security best practices, you can take the right next step and continue browsing the internet safely and confidently.